Overall sentiment in the fiberglass market remains cautious in 2023, highlighting ongoing economic uncertainty. The recession adds complexity, with potential consequences including layoffs and increased challenges in real estate and other markets. Broader economic factors such as inflation, interest rates and discretionary spending are also affecting demand for products such as boats and recreational vehicles.
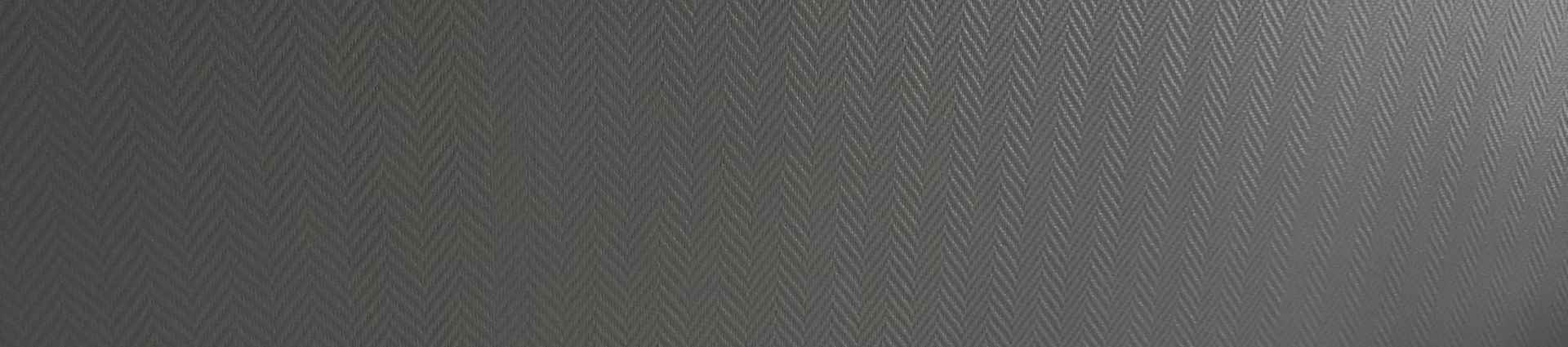
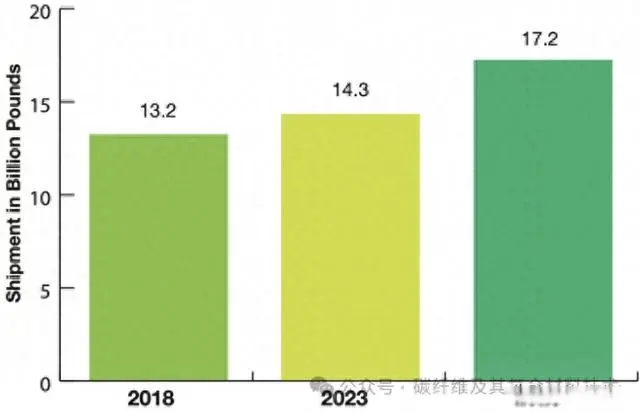
From an overall scale perspective, the demand for the fiberglass market will reach 14.3 billion pounds in 2023. The future appears to depend on navigating these complex market dynamics and adapting to changing economic conditions. According to Lucentel's forecast, demand for glass fiber will grow at a compound annual growth rate of approximately 4% from 2023 to 2028, as shown in the figure below.
One of the major challenges plaguing the composites industry in 2021 and 2022 is rising raw material prices due to supply chain issues, geopolitical events and the war in Ukraine. Resin and fiber prices also fell in 2023 due to a weak economy.
In the future, the demand for fiberglass will remain strong as demand continues to increase in sectors such as wind energy, electrical and electronics, automotive, marine and construction. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, wind energy will account for 22% of new installed electricity capacity in the United States in 2022. Wind energy is expected to grow rapidly, attracting $12 billion in capital investment in 2022, according to the Department of Energy. Since the passage of the Inflation Reduction Act, U.S. onshore wind energy installed capacity is expected to increase from 11,500 MW to 18,000 MW in 2026, an increase of nearly 60%, which will drive U.S. fiberglass composite consumption.
As environmental awareness increases, the fiberglass market's shift toward sustainability is a win for consumers who prioritize eco-friendly options. Recyclable fiberglass products help achieve a greener future. However, how to deal with the waste generated by these materials remains a big problem. For example, while most components of wind turbines are recyclable, turbine blades pose a challenge: the larger the blades, the greater the waste disposal problem.

The sustainable solution seems to be to use recyclable materials and recycle waste. Major OEMs are working with partners to trial recycling processes. General Electric, for example, has produced the world’s first fully recyclable wind turbine blade prototype, a new step in the industry’s transition to a circular economy. The 62-meter-long blades are made from Arkema’s 100% recyclable Elium® liquid thermoplastic resin and Owens Corning’s high-performance fiberglass.
Several fiberglass suppliers are also focusing on sustainability. China Jushi plans to invest US$812 million to build the world's first zero-carbon glass fiber factory in Huai'an, China. Toray Industries has developed a technology to recycle glass fiber-reinforced polyphenylene sulfide with properties similar to those of untreated resin. The company uses proprietary compounding technology to mix PPS resin with special reinforcing fibers.
Overall, the fiberglass market is undergoing significant transformational change, driven by growth, innovation and increased awareness of sustainability. The global fiberglass industry is expected to continue growing in the coming years, with key factors driving growth including increased demand in emerging economies, further adoption in the transportation and construction industries, and new applications in emerging industries.
Post time: Mar-27-2024

